22 September 2022
Updated: 28 October 2022
Different Types of Decentralized Exchanges Explained

Table of contents
- What Is a Decentralized Exchange?
- How Does a Decentralized Exchange Work?
- Order Book DEXs
- On-Chain Order Books
- Off-Chain Order Books
- On-Chain and Off-Chain Order Book Comparison
- Pros and Cons of Order Book DEXs
- Automated Market Makers (AMM)
- DEX Aggregators
- A Hybrid Future in DEXs
- Decentralized Trading on AtomicDEX
Table of contents
- What Is a Decentralized Exchange?
- How Does a Decentralized Exchange Work?
- Order Book DEXs
- On-Chain Order Books
- Off-Chain Order Books
- On-Chain and Off-Chain Order Book Comparison
- Pros and Cons of Order Book DEXs
- Automated Market Makers (AMM)
- DEX Aggregators
- A Hybrid Future in DEXs
- Decentralized Trading on AtomicDEX
Crypto market participants transfer assets worth billions of dollars every day. These assets move through crypto exchanges run by varying mechanisms and on various blockchain networks.
Crypto market participants transfer assets worth billions of dollars every day. These assets move through crypto exchanges run by varying mechanisms and on various blockchain networks.
Although the most popular crypto exchanges by trading volumes are centralized, the defining characteristic of blockchain tech lies in its decentralization. Decentralized exchanges are trading platforms that enable hassle-free transactions without lengthy KYC procedures.
What Is a Decentralized Exchange?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are crypto trading platforms that do not require any centralized third-party authority or custodian for their operations. These exchanges allow buyers and sellers to execute crypto transactions directly. DEXs are autonomous decentralized applications (dApps) that leverage smart contracts to self-execute agreements for crypto transactions.
Before the emergence of DEXs, crypto traders had to give up control of their digital assets and private keys to centralized crypto exchanges. DEXs allow traders to retain complete control of their crypto assets, private keys, and personal information since they are generally non-custodial and do not require any KYC verification. Many users consider this a significant advantage over centralized platforms.
How Does a Decentralized Exchange Work?
DEXs are similar to centralized exchanges (CEXs) in that they facilitate the sale and purchase of crypto assets. The major difference is that DEXs operate without intermediaries that validate and clear transactions.
A decentralized exchange uses automatically-executing protocols (smart contracts) on blockchains to facilitate trades between market participants without taking control of their crypto assets. DEXs handle transactions in one of three ways: an order book, an automated market maker, or a DEX aggregator.
Order Book DEXs
The order book model is one of the first-generation approaches in cryptocurrency trading. Order books maintain records of all open orders for buying and selling specific pairs of crypto assets. The order book comprises a list of buy orders which showcase traders' interest in purchasing or bidding for a crypto asset at a particular price, and sell orders indicating traders' willingness to sell an asset for a specific price. The DEX determines the crypto asset's current market price via automated analysis of the spread between buy and sell orders.
There are two approaches decentralized exchanges use in order book management: on-chain and off-chain.
On-Chain Order Books
These DEXs store their open order information directly on the underlying blockchain. The blockchain's ledger holds all transactions on the exchange and guarantees transparent operation. The on-chain approach allows traders to leverage their positions using assets borrowed from crypto lending platforms. Leveraged trading increases the profit potential of a trade but also increases the risk of incurring huge losses. This is because it raises the size of the trade, which must be repaid even if the exchange ends in a loss.
Additionally, there is also the risk of front-running. This is when nodes accessing transaction data about pending trades act as insiders and use pending trade data to transact in their favor.
Off-Chain Order Books
Off-chain order book-based DEXs perform transactions on the blockchain but store non-finalized transaction data elsewhere. A significant benefit of off-chain order books is their relatively high speed and improved privacy. Nonetheless, transferring transaction data to an external source has inherent security risks. Some well-known platforms that use off-chain order books include Binance DEX, 0x, and EtherDelta.
On-Chain and Off-Chain Order Book Comparison
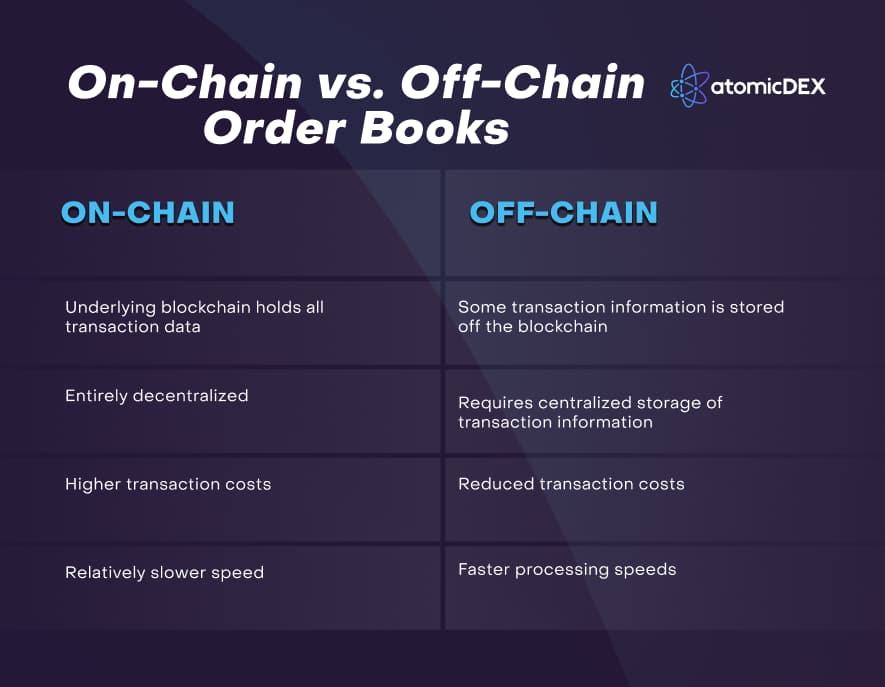
Pros and Cons of Order Book DEXs

Automated Market Makers (AMM)
The automated market maker (AMM) model uses smart contracts to address liquidity problems in crypto trading. AMMs leverage blockchain oracles, blockchain-based services used to collect information from crypto exchanges and external sources to determine the price of traded assets. With AMMs, rather than matching the buy orders with sell orders, smart contracts use liquidity pools. Users deposit funds into liquidity pools and get rewards for trades completed using their deposited crypto assets.
Liquidity pools provide users of AMM-based DEXs with a permissionless way to earn by letting them trade directly from non-custodial wallets. Some popular DEX platforms with AMM models include Uniswap, SushiSwap, and Kyber Network.
Pros and Cons of AMM DEXs
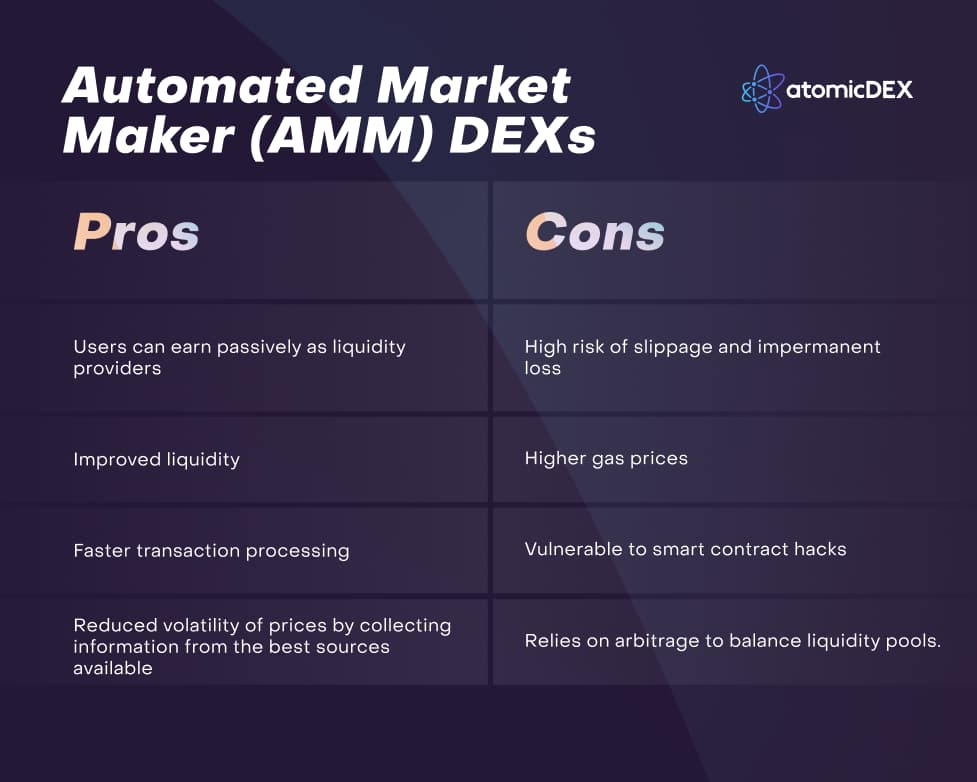
The AMM model has varying use cases across different platforms. An example is Uniswap, an AMM-based platform that allows instant swapping of Ethereum assets among users. Another example is Kyber, a universal exchange protocol that supports smart contracts built on any blockchain, and has a substantial liquidity pool for instant peer-to-peer transactions.
DEX Aggregators
The diverse and seemingly disjointed nature of crypto exchanges gave rise to DEX aggregators. The DeFi space consists of many platforms that use different blockchain networks, protocols, and methods of executing transactions. DEX aggregators address these interoperability issues to help solve the fragmentation problem and provide simplified user operations across platforms.
These exchange platforms combine liquidity from several DEXs to minimize slippage on large orders. They also support reduced trading fees and make crypto assets quickly available to users at the best possible prices. Some examples include the 1inch Exchange and DeversiFi.
Pros and Cons of DEX Aggregators

A Hybrid Future in DEXs
Although the order book and AMM models of DEXs have addressed most problems of centralized platforms, there is still a lot of growth potential.
A great solution for the drawbacks of the order book and AMM models is a hybrid solution that combines their strengths. This model will significantly increase global acceptance and adoption of DEXs.
Decentralized Trading on AtomicDEX
AtomicDEX is a non-custodial wallet, cross-chain bridge, and cross-chain/protocol DEX rolled into one app.
AtomicDEX offers the widest cross-chain/protocol support among all DEXs on the market. It supports native trading across multiple blockchains via P2P order books.
Start trading BTC, ETH and ERC-20 tokens, BNB and BEP-20 tokens, DOGE, MATIC, and many other popular cryptocurrencies.




