
Table of contents
Table of contents
A cross-chain bridge facilitates the exchange of information and crypto from one blockchain network to another. It enables interoperability across multiple blockchains.
There are thousands of cryptocurrencies and hundreds of blockchain networks available in the crypto space. While each cryptocurrency uses blockchain technology, many operate as standalone networks with their own communities and economies. Although these island networks are sometimes necessary, growing popularity in the Web3 space will see them become more interconnected.
Several cross-chain infrastructure solutions are gaining more recognition. However, there is still no way to move digital assets between blockchains with minimal friction. Over time, developers have created protocols to connect blockchains and allow for easy data flow between networks. These projects, called cross-chain bridges, directly increase the rate of cryptocurrency and blockchain adoption and usability because of their flexibility.
Cross-Chain Defined
A cross-chain bridge, like a physical bridge, links two points together. Cross-chain bridges enable seamless communication between blockchain networks by expediting asset and data exchanges across networks. Essentially, a cross-chain bridge is an application that supports blockchain interoperability.
Although blockchains have distinct protocols, rules, and governance structures, a cross-chain bridge provides a secure means for multiple networks to interoperate. Users employ cross-chain bridges to transfer tokens, smart contracts, and other types of information between otherwise unconnected blockchains.
Some of the benefits of cross-chain bridges include:
- Fast and seamless crypto-asset transactions
- Low operational difficulty
- Improved productivity and efficiency of existing crypto assets
- Improved security and better privacy
- Enhanced developer experience
How Do Cross-Chain Bridges Work?
Blockchain bridges (also known as cross-chain bridges or crypto bridges) use intercommunication mechanisms to transfer tokens and other internal data between blockchain networks. These bridges typically use some form of a mint-and-burn protocol. The protocol’s principle of operation is as follows:
- When tokens get transferred between Blockchain A and Blockchain B through a crypto bridge, they technically are not moved to a new chain.
- Instead, the tokens on Blockchain A are temporarily locked or burned, and an equivalent number of tokens get issued on Blockchain B.
Alternatively, some cross-chain bridges like AtomicDEX are peer-to-peer, meaning that two users complete cross-chain swaps with assets natively across blockchains. This removes the need for users to interact with a mint-and-burn protocol.
Wrapped Tokens and Cross-Chain Bridges
Often, cross-chain bridges involve the "wrapping" and "unwrapping" of a specific cryptocurrency. Although wrapping and unwrapping might seem like complex terms, they just mean that a protocol facilitates the usage of a specific cryptocurrency on its non-native blockchain. Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), an ERC20 token that has a 1:1 backing with Bitcoin, is one popular example of a wrapped token.
With WBTC, users transfer the liquidity of native Bitcoin to the non-native Ethereum blockchain. There are several reasons why users may wish to wrap cryptocurrencies using cross-chain bridges. More use cases and cheaper transaction fees are two common reasons why users choose to wrap/unwrap cryptocurrencies.
Why Is Cross-Chain Bridging Essential in the Crypto World?
Interoperability between blockchains is critical to the long-term success of cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and other blockchain use cases. With crypto bridges, users and developers do not need to overthink their choice of a platform when building apps or storing and trading crypto assets. Regardless of the preferred creation or storage network, the interoperability of blockchain networks creates more value for everyone.
Some of the improvements blockchain bridges bring to the crypto space include:
- Increased DeFi Capabilities — Many blockchains, like Bitcoin, hold significant value without an advanced DeFi ecosystem. However, this lack of access impedes the network’s ability to generate income from any holdings. Blockchain bridges help provide easy access to a broader DeFi ecosystem, more use cases, and increased opportunities.
- Scalability — As the number of transactions on blockchains increases, scalability issues arise. Blockchain bridges considerably help mitigate these issues without the need to switch networks. For example, bridges may link Layer 1 to Layer 2 blockchain protocols.
- Efficiency — Crypto users want to conduct transactions on blockchains with lower fees. Cross-chain bridges help reduce congestion on parent blockchains and save users significant money on gas fees.
- Web3 — The future of blockchain isn't tied to one ecosystem. Blockchain bridges add a critical factor required for developing and adopting multi-protocol decentralized applications.
Are Cross-Chain Bridges Safe?
Not all cross-chain bridges are created equal. Some bridges are safer than others.
Generally speaking, bridges that are trustless/decentralized are more secure than bridges that are trusted/centralized. Bridges that have fewer validators are easier for hackers to target than ones that have dozens or hundreds of validators. Centralized bridges also make it easier for validators to collude, which can lead to issues such as censorship of specific crypto addresses or theft of user funds.
Bridges that use P2P technology are generally more secure than ones that use AMM technology. With P2P bridges, neither users nor projects hold funds in smart contracts. With AMM bridges, funds held in smart contracts could be stolen by bad actors by exploiting unknown bugs in the protocol's code.
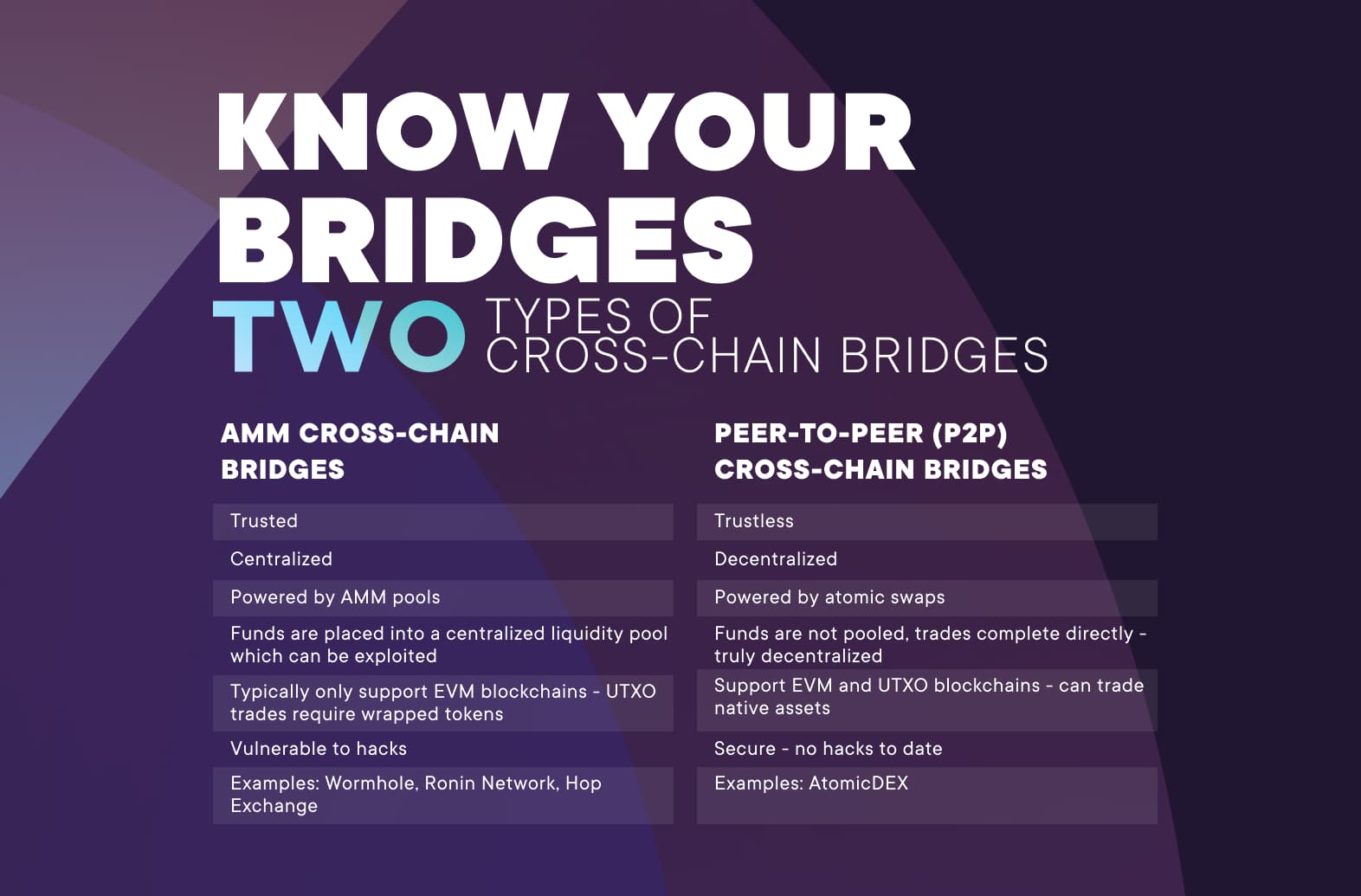
Two Main Types of Cross-Chain Bridges
There are two types of cross-chain bridges — trusted and trustless. Both have their own distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Trusted
Trust-based blockchain bridges, also known as federated bridges, are centralized bridges managed by a single entity or federation of mediators. The centralized bridge functions like a private or enterprise blockchain as users rely heavily on the operator to ensure bridge safety.
Trust-based bridges are a fast and cost-effective choice when performing transactions involving large quantities of crypto assets. However, it is crucial to understand that mediators get incentivized to keep transactions running and not identify and prevent security issues.
Trustless
Trustless bridges are decentralized blockchain bridges that rely on smart contracts or atomic swaps to operate. This type functions like known blockchains with individual networks contributing to transaction validation.
Trustless bridges give users a greater sense of security and flexibility when moving crypto assets. The use of non-custodial wallets in trustless bridges allows users to maintain complete control over their digital assets.
The Best Cross-Chain Bridges in 2023
Some of the best cross-chain bridges include the following:
- AtomicDEX — AtomicDEX is a non-custodial wallet, crypto bridge, and cross-chain DEX rolled into one app. Most crypto bridges link between just two blockchains. In contrast, AtomicDEX is a multi-way bridge, meaning it works with multiple blockchain protocols. For example, users can bridge between Ethereum and Bitcoin, Avalanche and Polygon, Bitcoin and Avalanche, Pologyon and Ethereum, as well as many other combinations. Users trade assets natively across blockchains via atomic swaps.
- Binance Bridge — The Binance Bridge enables users to exchange bridge crypto assets between the BNB Chain and other blockchains like Ethereum using BEP-20 tokens. The BNB Chain is an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible blockchain that facilitates low-cost smart contract transactions.
- Avalanche Bridge — The Avalanche Bridge facilitates the exchange of ERC-20 tokens from Ethereum to Avalanche’s C-Chain and vice versa. Avalanche built its crypto bridge precisely to scale financial transactions on the C-Chain.
- Polygon Bridge — The Polygon Bridge enables trustless transfers from Ethereum to Polygon and back without third-party risks or market liquidity limitations.
- Portal by Wormhole — Portal offers an unlimited volume of crypto-asset exchanges between various DeFi blockchains, such as Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Oasis, and Polygon.
- Multichain (AnySwap) — AnySwap is a fully-decentralized cross-chain communication protocol with an automated pricing and liquidity system, catering to a wide range of blockchain networks.
- Celer cBridge — Celer cBridge uses the Celer State Guardian Network to enable liquidity across different blockchains. Celer supports blockchain networks such as Ethereum, Astar, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, and Arbitrum.
- Umbria Narni Bridge — The Umbria Narni Bridge facilitates crypto transfers using liquidity pools, where assets are held across multiple blockchains.
Risks of Using Cross-Chain Bridges
Like any innovation designed to enhance efficiency, blockchain bridges also come with some risks.
- Transaction Issues — Bugs leading to failed transactions or loss of assets for unknown reasons are possible.
- Security Exploits — Some well-known AMM-based bridges have been hacked, which has led to billions of dollars in crypto losses for projects and end-users.
- Centralization — Trusted bridges have a centralized operator or group of operators who have the ability to reject swaps, censor specific crypto addresses, or even steal user funds.
- New Technology — Since cross-chain bridges are still in their infancy, developers have yet to create optimal solutions.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain bridges allow users to utilize and enjoy different blockchain protocols fluidly. These protocols offer significant market opportunities and a promising future for multi-chain operations, with bridges facilitating safe, quick, and cost-effective cross-chain interactions.
The ever-growing number of blockchain-based projects has made interoperability more vital than ever. With an AtomicDEX wallet, users can make cross-chain swaps across a wide range of blockchains, including Bitcoin and other UTXO chains, Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Polygon, Fantom, Harmony, and more.




